What is foot-and-mouth disease?
Foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) is a highly contagious viral disease of livestock causing fever followed by the development of vesicles (blisters) chiefly in the mouth and on the feet.
FMD is generally not lethal to adult animals, but it can kill young animals and cause serious production losses.
It affects cloven-hoofed animals (those with divided hoofs) including:
- cattle
- buffalo
- camels
- sheep
- goats
- deer
- pigs.
FMD is not considered a risk to public health as infection from animals to humans is extremely rare. FMD should not be confused with the human disease (hand, foot and mouth disease), caused by a different virus which commonly affects young children.
It is not present in Australia but is endemic throughout the Middle East, Africa, Asia and most of South America.
The most significant risk of entry of FMD into Australia is through illegal entry of meat and dairy products infected with the FMD virus and subsequent illegal feeding of these products (swill) to pigs.
Most countries would ban our livestock and livestock products as soon as foot-and-mouth disease is found. It is unlikely these restrictions would be lifted until Australia could prove that the disease had been eradicated.
The economic effects of an outbreak of FMD, would be enormous to individuals, the farming industry, and subsidiary and support industries.
Australia’s major livestock industries would be directly affected from export market closures and the disruption to production associated with the disease and response activities.
There would be significant flow-on economic losses and social impacts to many rural and regional businesses that rely on livestock industry revenue.
Further details on foot-and-mouth disease is available on the Australian Government Department of Agriculture, Fisheries and Forestry website.
Signs of foot-and-mouth disease
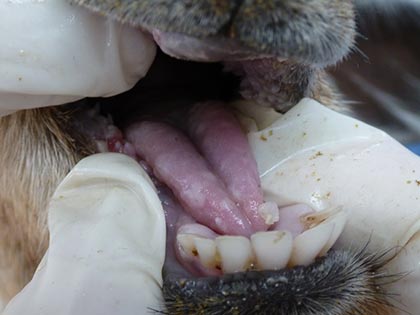
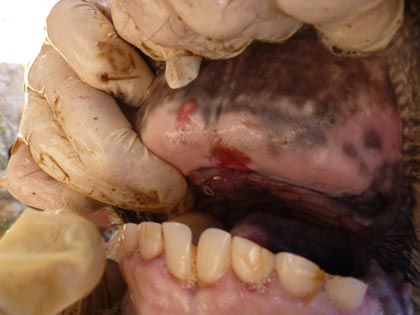
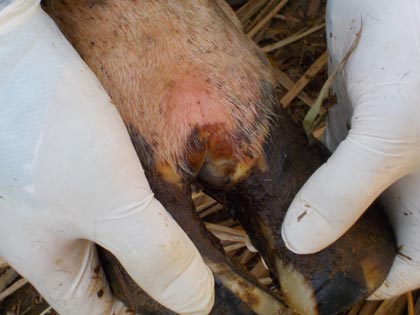
The following symptoms can be early signs of foot-and-mouth disease:
- lameness
- long strings of sticky saliva (cattle)
- blisters
More information
- Foot-and-mouth disease frequently asked questions
- Practical biosecurity steps on your farm
- Foot-and-mouth disease factsheet
The following websites have more information:
- Animal Health Australia
Emergency animal disease preparedness program including the AUSVETPLAN disease control strategy for FMD. - The European Commission for the Control of Foot-and-Mouth Disease
The commission is functioning under the auspices of the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. The web site provides information on various reports related to the FMD virus as well as recent news and resolutions. - World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH)
Information on foot-and-mouth disease and reported outbreaks around the world.
FMD is a notifiable exotic disease and any suspected or confirmed cases must be reported to Agriculture Victoria on the Emergency Animal Disease Hotline 1800 675 888 (24/7) or to your local Agriculture Victoria Animal Health and Welfare staff.