Citrus gall wasp
The citrus gall wasp (Bruchophagus fellis) is a native insect native to coastal regions around the border of Queensland and New South Wales. It has now spread throughout the eastern states, including South Australia and Victoria and has also been found in suburban Perth. The wasp produces lumpy, woody galls around its larvae on branches. The galls weaken the trees, reducing fruit size and yield and sometimes causing branch dieback.

How to spot citrus gall wasp
The citrus gall wasp produces characteristic woody galls which form around the developing larvae (Figure 1). These galls start to become visible in April and are easy to see by June. The wasps themselves are rarely seen as they are only 3mm in size and emerge out of small holes in the gall in early to late spring (Figure 2).

Spread
The natural host of the citrus gall wasp is the native Australian finger lime (Citrus australasica). However, it has now become adapted to cultivated citrus varieties such as lemons and grapefruit. The wasp doesn’t travel far from the original infestation, but the pest can spread from infested trees to nearby hosts and further distances through the movement of untreated, infested branches. Monitoring and control of citrus gall wasp is important to prevent further spread and damage.
Management
While citrus gall wasp can be difficult to control, there are things that can be done to minimise the damage. Understanding the lifecycle of these wasps helps us to understand the best time of year for controls (Figure 3).
Adult citrus gall wasps emerge from galls in spring – usually between mid-October to mid-December in southern Australia and are most abundant for about a month – from late October to mid-November. Once the wasp has emerged, it has about a week to mate and lay up to 100 eggs under the green bark of a citrus tree. The eggs hatch after 2 to 3 weeks and the larvae burrow deep into the stem and feed on citrus tissue.
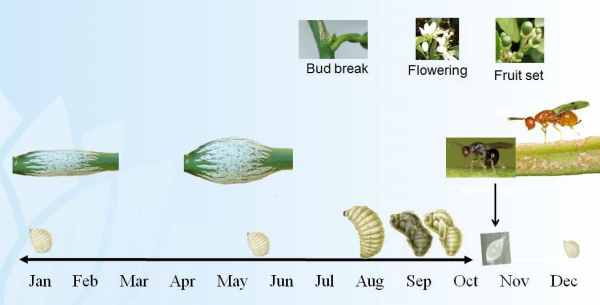
The tree reacts by producing extra cells in the area which ends up creating the distinctive galls. Larvae feed within the stem for about 9-10 months. The galls start to be seen from December through April and will gradually get bigger through autumn and winter. After a short pupation period in spring, the adults emerge from little holes in the galls and the cycle continues.
With this life cycle in mind, there are a few things to consider to manage the pest:
- Time your pruning: The best time to prune out galls is from April to June. Pruning in winter beyond June causes the tree to grow vigorously in spring and results in a flush of new foliage that the gall wasp prefers.
- Peel and reveal: Instead of pruning, slice the top off one side of the active gall using secateurs, a sharp knife or a potato peeler, remembering to face the blade away from your body. This exposes the larvae to air and kills them, without causing lasting damage to the tree. The best time to do this is mid to late winter.
- Burn or bake gall-infected off-cuts: Treat gall-affected branches before disposal by placing them in a well-sealed plastic bag in the sun to bake for a month or incinerate them. Wasps can still emerge from galls in pruning off-cuts. Disposing of gall off-cuts in normal household waste, a green verge collection or in garden bags will spread the pest to other areas.
- Fertilising: Avoid heavily fertilising of trees in winter or spring, which will promote excessive fresh growth that the wasp prefers.
- Don’t prune every year: Citrus gall wasps like to stay close to home and, in many cases, the same tree, so yearly pruning regimes which encourage fresh growth can perpetuate the gall wasp cycle.
- Check your trees: Galls in newly infested branches are small and difficult to see. Check for light green coloured shoots coming out at right angles from branches (spring to early autumn). Monitor all citrus trees all year round.
- Community involvement: involves your neighbours in monitoring and managing the pest as well. Coordinating control with your neighbours will mean fewer wasps laying eggs to create galls in the following season.
- Natural enemies: Parasitic wasps Megastigmus brevivalvus and M. trisulcus insert their eggs directly into the eggs of gall wasps where they slowly develop in the host larva, eventually killing it. Note that chemicals for gall wasp control will also affect the Megastigmus.
- Deter egg laying petroleum spray oils used against other citrus insect pests can deter gall wasp adults from laying eggs, as can calcined Kaolin clay.
Chemical control
Chemical control is often one of the methods available for plant pests as part of an integrated pest management program. More information is available from:
- your local nursery
- cropping consultants
- chemical resellers
- the pesticide manufacturer.
Information on currently registered or permitted chemicals can be found at the Australian Pesticide and Veterinary Medicine Authority (APVMA) website. Always consult the label and Safety Data Sheet before using any chemical product.
More information
- NSW Department of Primary Industries
- SA Department of Primary Industries and Regions
- WA Department of Primary Industries and Regional Development
- Sustainable Gardening Australia
Image credits
Figure 1: Agriculture Victoria
Figure 2: Department of Primary Industries and Regional Development (DPIRD), WA Department of Primary Industries, NSW.
Figure 3: Department of Primary Industries, NSW
Reporting an unusual plant insect pest or disease
Report any unusual plant pest or disease immediately using our online reporting form or by calling the Exotic Plant Pest Hotline on 1800 084 881. Early reporting increases the chance of effective control and eradication.
Please take multiple good quality photos of the pests or damage to include in your report where possible, as this is essential for rapid pest and disease diagnosis and response.
Your report will be responded to by an experienced staff member, who may seek more information about the detection and explain next steps.
Report online